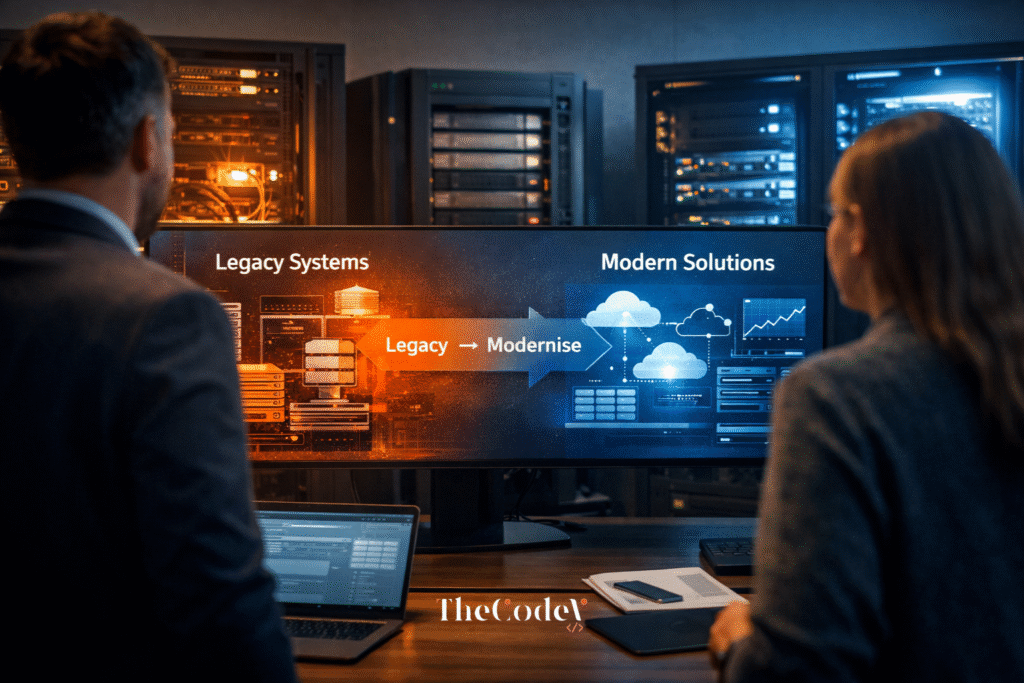
The Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer a futuristic concept — it’s the digital backbone of today’s connected world.
From smart homes to intelligent factories, IoT is driving a new era of automation and insight. In 2025, this technology is evolving faster than ever, becoming central to decision-making across nearly every sector. With the convergence of big data, AI, and real-time connectivity, IoT is reshaping how businesses operate, adapt, and compete.
Why 2025 Marks a Major Milestone for IoT
Over the past decade, IoT has shifted from experimental pilot projects to full-scale enterprise solutions. Now, in 2025, it’s reaching true maturity. The global number of connected devices is expected to surpass 30 billion this year [source: Statista]. This explosion is fuelled by faster networks, lower sensor costs, and the rising need for data-driven automation.
Organisations are harnessing this growth to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver smarter services. Whether it’s optimising traffic systems or monitoring patient vitals remotely, IoT is solving real-world problems at scale.
You can explore how we help businesses adopt smart solutions on our services page.
IoT and Its Role in the Modern Enterprise
Put simply, the Internet of Things is a system of connected devices that communicate and exchange data. These can be as small as a sensor in a shipping container or as complex as a cloud-integrated factory.
In 2025, IoT is tightly integrated with artificial intelligence, enabling real-time analysis, pattern recognition, and proactive response. This synergy is driving powerful IoT business applications in logistics, retail, agriculture, and more.
Discover how we implement scalable solutions for smart industries on our homepage.
Emerging IoT 2025 Trends to Watch
This year’s IoT 2025 trends signal a move towards edge computing, sustainability, and predictive intelligence. Devices are becoming more autonomous. Networks are becoming more resilient. And companies are demanding more secure, reliable systems that scale globally.
The coming sections of this guide will explore five leading use cases that are defining this transformation — from healthcare to smart cities and beyond.
IoT in Healthcare — Transforming Patient Outcomes
In 2025, Internet of Things (IoT) technology is redefining the future of healthcare. The convergence of wearable health monitors, AI-driven diagnostics, and smart hospital systems is enabling providers to deliver faster, safer, and more personalised care than ever before. As the NHS embraces digital transformation, IoT in healthcare is playing a central role in enhancing patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and long-term wellbeing.

Remote Monitoring and Smart Devices in Hospitals
One of the most impactful areas where IoT in healthcare is thriving is remote patient monitoring (RPM). Wearable devices such as smartwatches, biosensors, and adhesive health patches can now continuously collect vital signs like heart rate, oxygen saturation, temperature, and glucose levels. These real-time data streams are securely transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing for proactive interventions before conditions worsen.
For example, NHS Trusts across the UK are deploying virtual wards powered by IoT. According to NHS Digital, this model allows patients with chronic conditions like COPD or heart failure to be safely monitored at home using IoT-enabled devices. Nurses and clinicians receive automatic alerts if any patient vitals deviate from normal thresholds—minimising the risk of emergency hospitalisations.
At the hospital level, smart beds embedded with sensors can detect patient movement, pressure points, and breathing patterns, significantly reducing falls and improving post-surgical recovery. These smart systems can also integrate with Electronic Health Records (EHRs), ensuring continuous documentation and clinical visibility across departments.
AI-Driven Diagnostics and Predictive Health Analytics
The integration of IoT with artificial intelligence is another game-changer. Connected diagnostic devices such as portable ECG monitors, wireless ultrasound scanners, and IoT spirometers are enabling faster, AI-assisted clinical decisions—especially in A&E departments where time is critical.
In 2025, predictive analytics using IoT-generated data is helping clinicians identify early warning signs for sepsis, strokes, and even mental health crises. This is particularly vital in elderly care and paediatric medicine, where subtle physiological changes can be life-threatening.
The World Economic Forum’s 2024 report highlighted how UK hospitals using AI-IoT systems saw a 35% reduction in ICU readmission rates due to early intervention strategies driven by smart health insights.
Real-World Use Case: Manchester NHS Innovation Centre
A pioneering example is the Manchester NHS Foundation Trust, which launched a smart healthcare pilot in collaboration with the University of Manchester. Patients with type 2 diabetes were provided with IoT-connected glucose monitors and wearable fitness trackers. These devices, combined with behavioural nudges via mobile apps, led to a 25% improvement in glycaemic control within six months [HealthTech Magazine].
Moreover, these devices allowed GPs to access real-time patient health dashboards, improving engagement and reducing the burden on clinics. This aligns with NHS England’s long-term digital health plan, which prioritises remote-first care models using safe and scalable IoT frameworks.
Building a Connected Healthcare Ecosystem
A fully connected smart hospital ecosystem brings together IoT devices, cloud computing, and secure data networks to form a responsive, intelligent infrastructure. From inventory management using RFID-tagged equipment to automated sanitisation systems triggered by occupancy sensors, every element contributes to a safer, more efficient environment.
📊 Recommended Diagram: A visual diagram showing a smart hospital ecosystem including wearable patient devices, real-time dashboards, AI analysis hubs, RFID-tagged medical tools, and automated alert systems.
Alt text: “Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare hospitals”
Why IoT in Healthcare Matters for UK Businesses
IoT in healthcare is not just improving outcomes—it’s also reshaping how healthcare services are delivered and managed. Businesses developing IoT-powered health solutions or offering managed healthcare IT services stand to benefit enormously. At TheCodeV’s services page, we assist UK med-tech firms in building compliant, scalable IoT infrastructures tailored for NHS and private sector integration.
We also share detailed case studies that explore how real-world healthcare platforms have harnessed IoT to reduce costs, improve care, and gain competitive advantage.
IoT in Agriculture — The Rise of Smart Farming in 2025
The agricultural industry is undergoing a digital revolution. In 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) is central to the rise of smart farming, enabling unprecedented precision, sustainability, and profitability. Across the UK and beyond, farmers are leveraging connected devices and real-time analytics to monitor soil health, automate irrigation, and optimise harvests. These IoT business applications are redefining the future of food production.
Precision Agriculture with IoT Sensors
Traditional farming relied heavily on instinct and routine. Now, IoT sensors embedded in fields deliver continuous data on soil moisture, pH levels, nutrient content, and temperature. This granular insight empowers farmers to make real-time decisions tailored to the exact conditions of each plot.
In Cambridgeshire, for example, agritech start-ups are collaborating with local farms to deploy soil health monitoring systems. These systems connect to cloud dashboards, helping farmers pinpoint where fertilisers or watering are needed—avoiding waste and improving plant health.
Globally, this is echoed by large-scale farming operations using platforms that integrate satellite imagery, weather data, and IoT field sensors. According to AgFunderNews, precision agriculture powered by IoT can increase yields by up to 25%, while reducing input costs and water consumption significantly.
Automated Irrigation and Water Efficiency
Water scarcity is a pressing concern for agriculture, especially in climate-sensitive regions. IoT-powered smart irrigation systems automate watering schedules based on real-time soil and weather data. These systems can target specific rows or even individual plants, ensuring efficient use of every drop.
DEFRA’s Future Farming and Countryside Programme encourages UK farms to adopt such IoT business applications under the sustainable farming initiative. A pilot project in North Yorkshire, for instance, saw a 40% reduction in water usage when growers switched from manual irrigation to sensor-guided drip systems.
Further enhancements include drone-assisted irrigation mapping and AI algorithms that forecast optimal watering times, taking into account evapotranspiration rates and rainfall predictions.
Boosting Crop Yield and Disease Prevention
IoT’s ability to provide real-time crop health insights is transforming how farmers prevent disease and optimise yield. Drones equipped with multispectral cameras fly over fields, scanning for signs of blight, stress, or pest activity. These images are cross-referenced with sensor data and AI models to issue early warnings—allowing swift intervention before problems escalate.
Farmers in the East Midlands are now using connected drones and automated sprayers to conduct surgical interventions, reducing chemical usage and improving sustainability. Globally, companies like John Deere and Bayer are integrating IoT telemetry into their smart farming machinery to guide autonomous tractors and sprayers with pinpoint accuracy Forbes Agriculture IoT.
Growing Smarter with IoT
As agricultural demands grow and environmental regulations tighten, smart farming powered by the Internet of Things (IoT) offers a scalable solution. By aligning agronomic decisions with data-driven insights, UK farmers can lead the charge in building a resilient, efficient, and tech-enabled food system for the future.

Retail & Supply Chain Innovations Through IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming how retailers and supply chain operators function in 2025. From intelligent inventory tracking to personalised in-store experiences, IoT is enabling real-time decision-making, driving efficiency, and dramatically improving customer satisfaction. These IoT business applications are not only reshaping logistics but are also redefining how goods are displayed, sold, and delivered.
Connected Retail Experiences
Smart retail environments are now commonplace across the UK. Smart shelves embedded with weight sensors and RFID tags can detect when stock is low or misplaced, automatically triggering replenishment alerts. This ensures that popular products remain available and shelf-space is optimally used.
Retailers like Tesco and Sainsbury’s are trialling IoT-enabled footfall counters and customer behaviour analytics. These systems analyse heat maps of store activity, measuring dwell times and high-traffic zones to dynamically adjust product placement and promotional campaigns. According to RetailWeek, such implementations have led to an average sales lift of 12% in strategic aisles.
Smart changing rooms, equipped with IoT mirrors, are also gaining popularity in fashion outlets. These devices recommend accessories or sizes based on customer preferences and previous selections, enhancing engagement and driving upsells.
Supply Chain Visibility
Behind the retail frontlines, IoT is revolutionising supply chain logistics. RFID tags and GPS trackers enable full visibility of products from source to shelf. Retailers and warehouses can now monitor real-time location, temperature, humidity, and even shock impact during transit—essential for pharmaceuticals, fresh produce, and electronics.
Predictive stocking is another major benefit. Using AI integrated with IoT sensor data, warehouses forecast product demand based on real-time consumption rates, seasonality, and even external factors like weather trends. This allows for smarter procurement, reduced overstocking, and faster fulfilment cycles.
As reported by Supply Chain Digital, UK retailers adopting these systems have seen a 30–40% increase in inventory accuracy and a significant drop in logistics errors.
Amazon’s UK fulfilment centres are an exemplar, using IoT to streamline operations—from autonomous robots managing shelf layouts to real-time dashboards that coordinate picking, packing, and delivery.
The Future of Data-Driven Retail
As e-commerce and in-store experiences merge, the Internet of Things (IoT) offers the connective tissue that enables seamless integration. From understanding consumer behaviour to enhancing last-mile delivery, IoT is helping businesses stay agile, informed, and future-ready.
💡 Want to unlock the full potential of IoT in your retail or logistics business? Get in touch with TheCodeV and let’s transform your operations.
Security & Data Privacy in IoT Networks
As the Internet of Things (IoT) becomes the digital backbone of smart homes, cities, factories, and healthcare systems, security and data privacy concerns are at the forefront of IoT 2025 trends. With billions of interconnected devices transmitting sensitive information, protecting IoT networks from cyber threats is a critical priority for businesses and governments alike.
From botnet attacks on smart devices to data leaks from unsecured APIs, the risks are real—and growing. To foster trust and regulatory compliance, robust IoT security measures and data governance frameworks must be part of every implementation strategy.
Securing Billions of Devices
The scale of IoT in 2025 is staggering. Gartner predicts over 15 billion IoT devices will be active globally, many of which are vulnerable by design due to lightweight hardware and limited update capabilities.
Common vulnerabilities in IoT networks include:
Default passwords and poor authentication
Insecure APIs and data transfer protocols
Outdated firmware and lack of patching
Open network ports and weak access control
A notable example is the Mirai botnet, which exploited thousands of unsecured IoT cameras and routers to launch massive DDoS attacks—highlighting the real-world implications of weak security architecture.
Modern IoT networks counter these risks using end-to-end encryption (E2EE), secure boot mechanisms, and role-based device authentication. UK businesses are increasingly implementing Zero Trust architectures, where every device, user, and app must be verified before access is granted.
Further, edge security—securing data at the point of generation—has emerged as a leading strategy. By processing sensitive information locally (at the edge), businesses reduce exposure to cloud breaches while ensuring lower latency and faster response times.
According to ENISA, encrypting IoT data at rest and in transit, combined with secure firmware updates and monitoring, forms the backbone of a resilient IoT deployment.
Data Compliance in the UK
Security goes hand in hand with data privacy, especially under strict regulatory frameworks like the UK GDPR. Organisations handling consumer or industrial IoT data must ensure:
Data minimisation (only collecting what’s necessary)
Consent management for tracking and analytics
Right to access and deletion for personal data
Transparent processing with clear data policies
For businesses operating in the UK, this means ensuring all connected devices and platforms align with the Information Commissioner’s Office (ICO) standards and can demonstrate privacy by design.
In healthcare and smart city projects, where sensitive personal data is often involved, compliance isn’t optional—it’s a legal and ethical imperative. As TechRadar Pro notes, failure to secure IoT data properly could lead to fines of up to £17.5 million or 4% of global turnover, depending on the breach’s scale.
Organisations like the Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) recommend a layered defence strategy including device isolation, network segmentation, threat detection, and continuous risk assessment.
AI and IoT — A Powerful Partnership Shaping 2025 Industry
In 2025, the convergence of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is one of the most transformative forces in technology. Together, they form a symbiotic ecosystem where connected devices don’t just collect data — they analyse, learn, and act in real time. This AI + IoT fusion is at the forefront of IoT 2025 trends, enabling smarter factories, predictive urban systems, and autonomous infrastructures across the UK and globally.
By embedding intelligence directly into sensors, cameras, machines, and edge nodes, organisations are unlocking new efficiencies, reducing costs, and creating safer, more adaptive environments.
Intelligent Automation at the Edge
Traditionally, IoT devices would relay data to centralised cloud systems for processing. But with edge AI, computations now occur at the source — dramatically reducing latency, preserving bandwidth, and enhancing responsiveness. Edge-based inference enables real-time decision-making, a critical requirement for use cases like autonomous vehicles, robotic manufacturing arms, and emergency monitoring systems.
Take the example of smart transportation systems in Birmingham, where AI-enabled traffic sensors analyse congestion and automatically reprogram signal timings based on predictive flow models. This ensures smoother traffic management without the delay of cloud communication.
According to Gartner, more than 50% of enterprise-managed data is now generated and processed outside traditional data centres, largely driven by IoT + AI solutions deployed at the edge.
Predictive Intelligence and Anomaly Detection
AI’s greatest value in IoT lies in its ability to detect anomalies and predict outcomes. In industrial settings, this means spotting micro-failures in machine vibrations, temperature deviations, or irregular sensor feedback before they escalate into breakdowns.
For instance, UK-based manufacturers using NVIDIA’s AI-IoT development kits have deployed predictive maintenance models that reduce equipment failure by up to 40%, as highlighted in the NVIDIA Blog. These systems learn from historical IoT sensor data and flag unusual behaviour patterns, prompting preemptive inspections.
This same technology is used in smart grids, where AI algorithms detect consumption spikes or transformer anomalies, allowing energy providers to isolate and address issues before outages occur — a major benefit for energy-reliant urban centres.
Scalable Learning Across Devices
One of the most compelling IoT 2025 trends is federated learning, where AI models are trained collaboratively across multiple devices without transferring raw data. This not only enhances privacy (critical for GDPR compliance in the UK) but also allows models to adapt locally while sharing collective intelligence across networks.
In smart homes, for example, connected appliances can learn user behaviour individually but improve through shared patterns — such as identifying the best energy-saving routines based on aggregated household data across a region.
As noted by MIT Technology Review, AI’s deep learning capabilities are key to the evolution of IoT into context-aware systems that anticipate needs rather than just respond to inputs.
Future-Ready with AI and IoT
As industries strive for autonomy, sustainability, and resilience, the partnership between AI and the Internet of Things (IoT) will be pivotal. By embedding cognition into connected devices, businesses in 2025 can move from reactive responses to proactive, predictive intelligence.
💡 Want to discover how AI can elevate your IoT infrastructure? Speak with TheCodeV and let us help you deploy smart, scalable, and secure AI-IoT solutions.
IoT and Sustainability in 2025 — A Greener Future Through Smart Innovation
In 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) is no longer just a technological advancement—it’s a cornerstone of global sustainability efforts. With climate goals accelerating and regulations tightening, IoT-driven solutions are empowering governments, businesses, and individuals to monitor, reduce, and optimise their environmental impact. As part of broader IoT 2025 trends, sustainability-focused applications are transforming energy systems, carbon tracking, transport, and the built environment.
From reducing emissions to conserving energy, the IoT is proving that digital transformation and environmental responsibility go hand in hand.
Green IoT Solutions
IoT is powering smarter infrastructure to achieve environmental gains. Smart grids, for instance, use real-time IoT data from electricity meters, renewable generators, and consumption endpoints to balance supply and demand efficiently. In the UK, Smart Energy GB has rolled out millions of connected smart meters, allowing households to reduce energy consumption through accurate, real-time insights.
In buildings, IoT-enabled energy management systems automate lighting, HVAC, and appliance usage based on occupancy and usage patterns. For example, UK-based corporate campuses now deploy AI-linked IoT sensors that detect vacant meeting rooms and adjust lighting and temperature automatically—cutting carbon emissions and electricity costs by over 25%.
Water conservation is also seeing impact through IoT leakage detection sensors in public utilities. These systems help water companies locate and resolve leaks rapidly, preserving this vital resource in drought-sensitive regions.
IoT even supports sustainable agriculture by reducing fertiliser and water usage, aligning with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) on clean water, climate action, and responsible consumption UN SDGs.
Driving Net-Zero with Smart Tech
Achieving net-zero carbon targets is impossible without accurate and ongoing measurement. IoT carbon monitoring systems offer granular insights into emissions at the asset, building, and fleet levels. From factories tracking CO₂ output to logistics firms monitoring vehicle emissions, IoT enables real-time carbon audits and automated reporting.
In London, transport authorities are deploying IoT-powered air quality sensors across major roads and underground stations to identify pollution hotspots and assess the success of low-emission zones. These systems not only drive smarter policy but also feed data into NHS alerts for vulnerable groups.
Meanwhile, transport companies are adopting connected EV fleet solutions. These platforms use IoT to optimise route planning, charging schedules, and driver behaviour to maximise battery efficiency and reduce environmental impact—fully aligning with the UK’s 2035 zero-emission vehicle goals.
The Carbon Trust notes that such innovations are key to closing the gap between sustainability pledges and measurable impact.
Real Impact with TheCodeV
Sustainability doesn’t just require commitment—it demands real-time action and accountability. At TheCodeV, we help organisations design and deploy IoT platforms that support net-zero roadmaps, from smart grid integrations to intelligent facility management systems.
Whether you’re a green tech startup or a city authority, our team delivers custom solutions that are scalable, secure, and measurable. Connect with us via our homepage or contact page to learn how our IoT systems can make your operations cleaner and smarter.
Future Outlook — Where is IoT Heading Beyond 2025?
As we move past 2025, the Internet of Things (IoT) is poised for even more radical transformation. The landscape that once centred on sensor-based monitoring is now evolving into a dynamic, intelligent ecosystem powered by 6G networks, quantum-secured systems, and deeply embedded AI-IoT convergence. These upcoming developments represent the next phase of IoT 2025 trends—shifting from connected to cognitive environments, and from automation to full autonomy.
With global infrastructure adapting rapidly, and organisations prioritising real-time intelligence, the IoT of the future will be hyper-personalised, ultra-secure, and decentralised by design.
Hyperconnectivity with 6G
While 5G has enabled many of today’s smart systems, 6G will be the backbone of future IoT deployments. With projected speeds up to 100 times faster than 5G and near-zero latency, 6G will empower trillions of connected devices to communicate simultaneously in real time.
According to the World Economic Forum, 6G will support holographic communication, tactile internet, and ambient intelligence—all of which will underpin next-gen IoT applications in areas like remote surgery, smart manufacturing, and spatial computing.
These ultra-fast networks will be essential for enabling autonomous systems to respond instantly without relying on centralised cloud platforms—ushering in a new wave of self-operating machines and urban infrastructure.
Quantum Security and Decentralised Trust
With the vast expansion of IoT comes heightened security risk. As classical encryption methods face obsolescence, quantum-resistant cryptography is becoming critical. Researchers featured in IEEE Future Technologies highlight how quantum computing could compromise current IoT protocols—prompting an urgent shift toward post-quantum IoT security frameworks.
Meanwhile, decentralised trust systems such as blockchain-integrated IoT are growing in prominence. These ensure device-level authentication, tamper-proof logs, and self-verifying smart contracts—critical for industries like logistics, finance, and public infrastructure.
Together, quantum security and decentralised networks will form the backbone of resilient IoT systems in an increasingly hostile cyber environment.

Consulting on Internet of Things (IoT) strategy with TheCodeV
Cognitive AI and Fully Autonomous Systems
Beyond analytics, AI in IoT is evolving into an agent of decision-making and adaptive control. We’re witnessing the rise of autonomous ecosystems—factories that self-optimise, transport systems that self-direct, and buildings that self-regulate in real time.
In fact, by 2030, Gartner predicts that over 60% of industrial decisions will be made by machine-led cognitive systems trained on vast volumes of IoT data. These systems will not only detect anomalies or forecast maintenance—they’ll act independently to resolve them.
Imagine an energy grid that auto-routes surplus power based on predictive consumption or an emergency response drone fleet that mobilises before first responders are even alerted. These are not hypotheticals—they are fast-approaching realities already being tested in the UK, EU, and Asia.
Wired UK notes that such self-governing IoT frameworks will underpin the next stage of smart infrastructure—from climate adaptation to autonomous healthcare delivery.
Final Thoughts: Harnessing the Internet of Things (IoT) in 2025 and Beyond
As 2025 unfolds, the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to revolutionise how industries operate, innovate, and compete. From smart healthcare that monitors patients remotely, to intelligent factories optimising production lines, and sustainable cities reducing carbon footprints, IoT is the digital thread weaving intelligence into every aspect of business and infrastructure.
We’ve explored how smart manufacturing, retail, agriculture, urban development, supply chain logistics, and energy management are being transformed through IoT solutions. Across each of these verticals, one trend is clear: success belongs to those who harness real-time data, automation, and AI-integrated IoT ecosystems.
At TheCodeV, we specialise in developing scalable, secure, and future-ready IoT platforms. Whether you’re a startup building your first smart product or a large enterprise modernising operations, our team brings deep expertise in edge computing, AI integration, and compliance-first infrastructure design.
We don’t just deliver solutions—we become your technology partner for long-term innovation.
Ready to Build the Future of IoT?
🚀 Let’s turn your vision into a connected reality.
Whether you need an end-to-end IoT architecture or a proof-of-concept to pitch to investors, we’re here to help. Explore our services, learn from our case studies, or book a consultation with our specialists today.